
Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive brain disease, presents unique challenges for individuals and their loved ones. As questions and concerns arise, seeking clarity becomes crucial. Here, we address some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Alzheimer’s disease to provide insight and support.
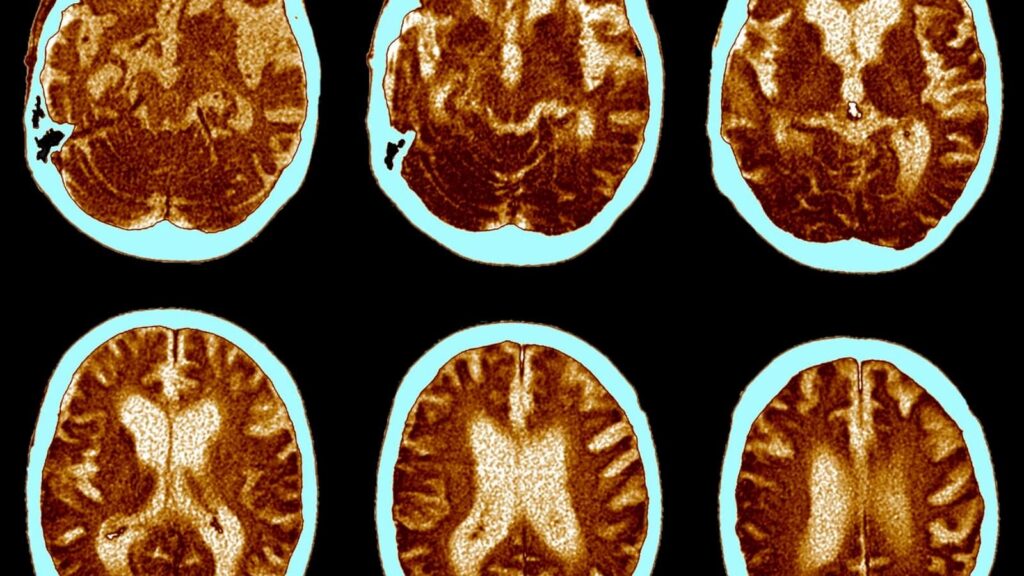
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the gradual decline of cognitive function, particularly memory, thinking skills, and the ability to perform daily tasks. It is the most common cause of dementia, accounting for approximately 60-80% of cases.
The exact cause of Alzheimer’s disease remains unknown, but researchers believe it involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Abnormal protein deposits in the brain, known as amyloid plaques and tau tangles, are hallmark features of Alzheimer’s and contribute to nerve cell damage and communication breakdown in the brain.
Dementia serves as an umbrella term describing symptoms affecting cognitive abilities, including memory loss, reasoning, communication, and the ability to perform daily tasks. Alzheimer’s disease is a common cause of dementia. Among the elderly, Alzheimer’s is the most prevalent cause of dementia. Dementia can also manifest as frontotemporal disorders, Lewy body dementia, and vascular dementia. Learn more about Alzheimer’s disease and the differences between dementia.
Early signs of Alzheimer’s disease often include memory loss, especially of recent events or conversations, difficulty with problem-solving and planning, challenges with language and communication, confusion about time or place, and changes in mood or personality.
While genetics can play a role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease, it is not solely determined by genetics. Having a family history of Alzheimer’s can increase one’s risk, but many other factors, such as age, lifestyle, and environmental influences, also contribute to the disease’s onset.
Early-onset Alzheimer’s disease, although uncommon, can result from genetic variations or alterations in specific genes. If such a variant is inherited, children will typically — but not always — develop the disease. For other cases of early-onset Alzheimer’s, studies indicate the involvement of other genetic factors.
There is no definitive way to prevent Alzheimer’s disease, but certain lifestyle choices may help reduce the risk or delay its onset. These include staying mentally and socially active, engaging in regular physical exercise (One study found that cognitive decline is almost twice as common among inactive adults compared to those who are active), maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, managing chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, and avoiding tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption.
Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease. Treatment primarily focuses on managing symptoms, slowing disease progression, and improving quality of life. Medications may help temporarily improve cognitive function or manage behavioral symptoms, but they do not stop the underlying neurodegenerative process.
Caregivers play a vital role in supporting individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. It is equally as important for caregivers to take care of themselves as they look over those affected by dementia or Alzheimer’s. Additionally, getting involved in Alzheimer’s advocacy and research efforts can make a meaningful impact in raising awareness, advancing scientific understanding, and advocating for policy changes. Opportunities include participating in clinical trials, fundraising events, and awareness campaigns.
There are several resources that you can look into for support, information, and financial assistance:
Ready to explore innovative ways to support individuals affected by Alzheimer’s? Join Resilia’s community of clinical and creative professionals to discover how arts-based treatments can enhance emotional resilience, cognition, and overall well-being.
Let’s embark on a journey together to create meaningful experiences and products that make a difference in the lives of those living with Alzheimer’s. Contact us today!
We use cookies to give you the best online experience. By using this website you agree with our cookie policy.